jupyterhub on kubernetes(3)
在前面两篇中已经配置好了jupyterhub自身的两大组件proxy和hub,这次主要说下,由hub控制kubespawner以singleuser镜像为每个用户启动pod,默认的镜像可能自带的工具比较少,所以需要自定义合适的通用镜像。
下面这个就是jupyterhub的架构图,结合上面两篇文章,理解下jupyterhub的工作原理。
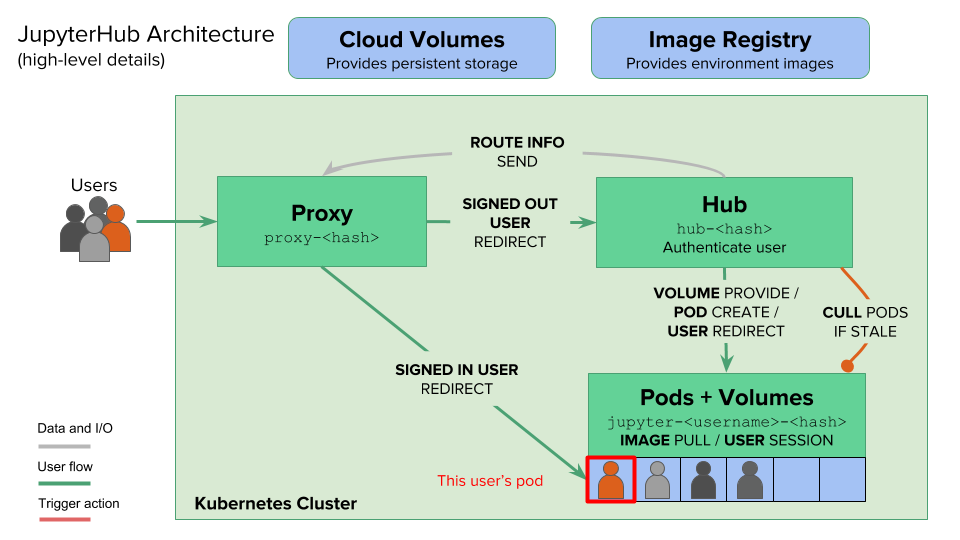
singleuser镜像主要自定义默认自带哪些python包、linux工具、和pod销毁之后数据的持久化问题(包括私有卷和共享卷)、镜像启动后CPU和内存的资源使用、更改启动后的默认用户和添加sudo权限等。
资源设置
这里对CPU和内存进行资源限制和保证,其实对应的就是kubernetes中的资源配置。limit就是最大不能超过,guarantee是保证,可以理解为最小资源。
singleuser:
memory:
limit: 3G
guarantee: 1G
cpu:
limit: 1.5
guarantee: 0.5
镜像设置
可以在github上面看到singleuser-sample默认的Dockerfile文件,是基于base-notebook镜像编写的。
FROM jupyter/base-notebook:27ba57364579
# conda/pip/apt install additional packages here, if desired.
# pin jupyterhub to match the Hub version
# set via --build-arg in Makefile
ARG JUPYTERHUB_VERSION=0.8
RUN pip install --no-cache jupyterhub==$JUPYTERHUB_VERSION
需要弄清楚就的查看base-notebook的Dockerfile文件,幸好在github上可以找到官方的源码。
FROM ubuntu@sha256:84c334414e2bfdcae99509a6add166bbb4fa4041dc3fa6af08046a66fed3005f
LABEL maintainer="Jupyter Project <jupyter@googlegroups.com>"
USER root
# Install all OS dependencies for notebook server that starts but lacks all
# features (e.g., download as all possible file formats)
ENV DEBIAN_FRONTEND noninteractive
RUN apt-get update && apt-get -yq dist-upgrade \
&& apt-get install -yq --no-install-recommends \
wget \
bzip2 \
ca-certificates \
sudo \
locales \
fonts-liberation \
&& apt-get clean \
&& rm -rf /var/lib/apt/lists/*
RUN echo "en_US.UTF-8 UTF-8" > /etc/locale.gen && \
locale-gen
# Install Tini
RUN wget --quiet https://github.com/krallin/tini/releases/download/v0.10.0/tini && \
echo "1361527f39190a7338a0b434bd8c88ff7233ce7b9a4876f3315c22fce7eca1b0 *tini" | sha256sum -c - && \
mv tini /usr/local/bin/tini && \
chmod +x /usr/local/bin/tini
# Configure environment
ENV CONDA_DIR=/opt/conda \
SHELL=/bin/bash \
NB_USER=jovyan \
NB_UID=1000 \
NB_GID=100 \
LC_ALL=en_US.UTF-8 \
LANG=en_US.UTF-8 \
LANGUAGE=en_US.UTF-8
ENV PATH=$CONDA_DIR/bin:$PATH \
HOME=/home/$NB_USER
ADD fix-permissions /usr/local/bin/fix-permissions
# Create jovyan user with UID=1000 and in the 'users' group
# and make sure these dirs are writable by the `users` group.
RUN useradd -m -s /bin/bash -N -u $NB_UID $NB_USER && \
mkdir -p $CONDA_DIR && \
chown $NB_USER:$NB_GID $CONDA_DIR && \
chmod g+w /etc/passwd /etc/group && \
fix-permissions $HOME && \
fix-permissions $CONDA_DIR
USER $NB_UID
# Setup work directory for backward-compatibility
RUN mkdir /home/$NB_USER/work && \
fix-permissions /home/$NB_USER
# Install conda as jovyan and check the md5 sum provided on the download site
ENV MINICONDA_VERSION 4.3.30
RUN cd /tmp && \
wget --quiet https://repo.continuum.io/miniconda/Miniconda3-${MINICONDA_VERSION}-Linux-x86_64.sh && \
echo "0b80a152332a4ce5250f3c09589c7a81 *Miniconda3-${MINICONDA_VERSION}-Linux-x86_64.sh" | md5sum -c - && \
/bin/bash Miniconda3-${MINICONDA_VERSION}-Linux-x86_64.sh -f -b -p $CONDA_DIR && \
rm Miniconda3-${MINICONDA_VERSION}-Linux-x86_64.sh && \
$CONDA_DIR/bin/conda config --system --prepend channels conda-forge && \
$CONDA_DIR/bin/conda config --system --set auto_update_conda false && \
$CONDA_DIR/bin/conda config --system --set show_channel_urls true && \
$CONDA_DIR/bin/conda update --all --quiet --yes && \
conda clean -tipsy && \
rm -rf /home/$NB_USER/.cache/yarn && \
fix-permissions $CONDA_DIR && \
fix-permissions /home/$NB_USER
# Install Jupyter Notebook and Hub
RUN conda install --quiet --yes \
'notebook=5.2.*' \
'jupyterhub=0.8.*' \
'jupyterlab=0.31.*' \
&& conda clean -tipsy && \
jupyter labextension install @jupyterlab/hub-extension@^0.8.0 && \
npm cache clean && \
rm -rf $CONDA_DIR/share/jupyter/lab/staging && \
rm -rf /home/$NB_USER/.cache/yarn && \
fix-permissions $CONDA_DIR && \
fix-permissions /home/$NB_USER
USER root
EXPOSE 8888
WORKDIR $HOME
# Configure container startup
ENTRYPOINT ["tini", "--"]
CMD ["start-notebook.sh"]
# Add local files as late as possible to avoid cache busting
COPY start.sh /usr/local/bin/
COPY start-notebook.sh /usr/local/bin/
COPY start-singleuser.sh /usr/local/bin/
COPY jupyter_notebook_config.py /etc/jupyter/
RUN fix-permissions /etc/jupyter/
# Switch back to jovyan to avoid accidental container runs as root
USER $NB_UID
从Dockerfile文件中可以看到,是基于ubuntu操作系统构建的镜像,以切换用户整个文件文件可以分为几块去查看:
- 以root用户,使用apt-get安装操作系统依赖包;wget安装tini二进制文件;配置关于用户的环境变量并创建这个普通用户,修改文件夹权限。
- 以普通用户创建工作目录,安装miniconda,使用conda安装jupyter相关的包并配置相关包的字体和配置文件。
- 以root用户暴露8888端口,切换工作目录,设置启动命令,拷贝相关文件到容器中。
- 最后在切换成普通用户。
弄清楚上面这个Dockerfile的每一步的含义后,就可以动手去自定义自己需要的软件包。
- 使用apt-get安装系统软件包vim,build-essential(这是一组开发相关的包),git, wget。
RUN apt-get update && apt-get -yq dist-upgrade \
&& apt-get install -yq --no-install-recommends \
vim \
build-essential \
git \
wget \
bzip2 \
ca-certificates \
sudo \
locales \
fonts-liberation \
&& apt-get clean \
&& rm -rf /var/lib/apt/lists/*
- 修改用户环境变量为jupyter,也就是启动后的普通用户。
ENV CONDA_DIR=/opt/conda \
SHELL=/bin/bash \
NB_USER=jupyter \
NB_UID=1000 \
NB_GID=100 \
LC_ALL=en_US.UTF-8 \
LANG=en_US.UTF-8 \
LANGUAGE=en_US.UTF-8
- 在创建普通用户jupyter之后,增加下面的命令,添加sudo权限。
RUN echo "jupyter ALL=(ALL) NOPASSWD: ALL" > /etc/sudoers.d/jupyter && \
chmod 0440 /etc/sudoers.d/twer
- 安装miniconda之后,配置conda的下载源为清华源。
RUN cd /tmp && \
wget --quiet https://repo.continuum.io/miniconda/Miniconda3-${MINICONDA_VERSION}-Linux-x86_64.sh && \
echo "0b80a152332a4ce5250f3c09589c7a81 *Miniconda3-${MINICONDA_VERSION}-Linux-x86_64.sh" | md5sum -c - && \
/bin/bash Miniconda3-${MINICONDA_VERSION}-Linux-x86_64.sh -f -b -p $CONDA_DIR && \
rm Miniconda3-${MINICONDA_VERSION}-Linux-x86_64.sh && \
$CONDA_DIR/bin/conda config --system --prepend channels conda-forge && \
$CONDA_DIR/bin/conda config --system --set auto_update_conda false && \
$CONDA_DIR/bin/conda config --system --set show_channel_urls true && \
$CONDA_DIR/bin/conda config --add channels https://mirrors.tuna.tsinghua.edu.cn/anaconda/pkgs/free/ && \
$CONDA_DIR/bin/conda config --add channels https://mirrors.tuna.tsinghua.edu.cn/anaconda/pkgs/main/ && \
$CONDA_DIR/bin/conda update --all --quiet --yes && \
conda clean -tipsy && \
rm -rf /home/$NB_USER/.cache/yarn && \
fix-permissions $CONDA_DIR && \
fix-permissions /home/$NB_USER
- 使用conda安装scipy、matplotlib、scikit-learn、pandas、seaborn、xlrd、numpy包,给conda安装的matplotlib包添加字体,并且添加matplotlibrc配置文件。
RUN conda install --quiet --yes \
'notebook=5.2.*' \
'jupyterhub=0.8.*' \
'jupyterlab=0.31.*' \
'scipy' \
'matplotlib' \
'scikit-learn' \
'pandas' \
'seaborn' \
'xlrd' \
'numpy' \
&& conda clean -tipsy && \
jupyter labextension install @jupyterlab/hub-extension@^0.8.0 && \
npm cache clean && \
rm -rf $CONDA_DIR/share/jupyter/lab/staging && \
rm -rf /home/$NB_USER/.cache/yarn && \
fix-permissions $CONDA_DIR && \
fix-permissions /home/$NB_USER
ADD SimHei.ttf /opt/conda/lib/python3.6/site-packages/matplotlib/mpl-data/fonts/ttf/SimHei.ttf
ADD matplotlibrc /opt/conda/lib/python3.6/site-packages/matplotlib/mpl-data/matplotlibrc
Dockerfile命令中有ADD和COPY命令对应的文件,都可以从github上下载下来和Dockerfile一起放到一个新文件夹basenodebookimage中,在这个文件夹中build镜像,下面是文件夹中的文件名称。
Dockerfile fix-permissions jupyter_notebook_config.py
matplotlibrc SimHei.ttf start-notebook.sh start.sh
start-singleuser.sh
这会就剩下构建base-notebook镜像,然后基于这个再构建singleuser镜像,push到自己的私有镜像仓库,手动在每个kubernetes的工作节点手动pull下来,否则在pre-pull执行的时候会显示找不到镜像,然后在config.yaml中指定singleuser的镜像。
cd basenodebookimage
docker build -t mydocker.registry.com/jupyterhub/base-notebook:v1
cd singleuserimage
cat Dockerfile
---
FROM mydocker.registry.com/jupyterhub/base-notebook:v1
# conda/pip/apt install additional packages here, if desired.
# pin jupyterhub to match the Hub version
# set via --build-arg in Makefile
ARG JUPYTERHUB_VERSION=0.8
RUN pip install --no-cache jupyterhub==$JUPYTERHUB_VERSION
---
docker build -t mydocker.registry.com/jupyterhub/k8s-singleuser:v1
docker push mydocker.registry.com/jupyterhub/k8s-singleuser:v1
接下来配置config.yaml文件,指定singleuser使用的镜像为刚才构建的镜像。
singleuser:
image:
name: mydocker.registry.com/jupyterhub/k8s-singleuser
tag: v1
持久化设置
为每个用户启动的pod都会在空闲的时候回收,下次启动的时候,用户的文件就会丢失,所以要挂载一个kubernetes的pvc作为私用卷当作用户的工作目录,另一个pvc当作共享卷挂载到另一个目录,首先就要确保kubernetes当中正确配置了storageClass,这里根据可用和灵活性选择了glusterfs作为storageClass的底层存储技术,heketi作为kubernetes和glusterfs的中间件,kuberntes内置的存储类可用调用heketi在glusterfs上面创建卷并且挂载到对应的pod上,storageClass的创建在部署kubernetes文章中,这里不具体说了,下面配置singleuser的storage。
singleuser:
storage:
homeMountPath: /home/jupyter
capacity: 5G
dynamic:
storageClass: glusterfs
yaml文件中storageClass的值是kubernetes中storageClassName的值,私有卷的大小是5G,挂载的目录是/home/jupyter,就是在base-notebook的Dockerfile中配置的那个普通用户的home目录。接下来是配置共享卷,私有卷是自动创建的,但是共享卷得先手动创建好,然后每个用户pod启动的时候直接挂载就行,所以这里要先写kubernetes的yaml文件claim-share.yaml创建pvc。
kind: PersistentVolumeClaim
apiVersion: v1
metadata:
name: claim-share
namespace: kube-public
spec:
accessModes:
- ReadWriteMany
volumeMode: Filesystem
resources:
requests:
storage: 10G
storageClassName: glusterfs
挂载的类型是文件系统,大小10G,指定是在kube-public的命名空间,jupyterhub的所有东西都是安装在kube-public中,或者换个新的也一样。
kubectl create -f claim-share.yaml
创建好之后,在config.yaml中配置这个共享卷的挂载信息,挂载到/mnt下面。
singleuser:
storage:
extraVolumes: [
{
'name': 'volume-share',
'persistentVolumeClaim': {
'claimName': 'claim-share'
}
}
]
extraVolumeMounts: [
{
'mountPath': '/mnt',
'name': 'volume-share'
}
]
其他设置
每个用户启动的pod都挂载了一个私有卷,个人的信息最好都保存在这个卷上,所以使用pip安装包的时候,需要指定安装位置和信任的安装源,私有卷是挂载在home目录上面,所以在docker镜像里面去做这个配置,会被覆盖掉,但是jupyterhub已经考虑到这个问题了,使用下面的lifecycleHooks。
singleuser:
lifecycleHooks:
postStart:
exec:
command: ["/bin/bash","-c",
"mkdir -p .pip && echo -e '[install]\ninstall-option=--prefix=
~/.local\ntrusted-host=mirrors.aliyun.com\n\n[global]\n
index-url = http://mirrors.aliyun.com/pypi/simple/\n' > .pip/pip.conf"]
在values.yaml文件中又一个prepull,是一个一次性的job任务,为了提前拉取镜像,这个在values.yaml文件中有一个pause的镜像,了解kubernetes的都知道,这个是一个pod的基础镜像,需要修改成自己镜像仓库或者可以访问到的其他源,比如阿里云的。
prePuller:
pause:
image:
name: registry.cn-hangzhou.aliyuncs.com/google_containers/pause-amd64
tag: '3.0'
安装启动
到此一切就准备的差不多了,下来就是使用helm工具部署到kubernetes上面。
helm install ./jupyterhub \
--version=v0.7-e6b48f6 \
--name=data8-jupyterhub \
--namespace=kube-public \
-f config.yaml
version的值就是Chart.yaml中的值,name是用来区别的,和docker命令中的name意义一样,namespace和上面创建共享卷的一样都是kube-public,最后指定自定义的配置文件config.yaml,这样才能使刚才一系列的配置生效,成功之后可以使用下面命令查看,也可以去kubernetes的dashboard中查看启动情况。
>: helm ls --all
NAME REVISION UPDATED STATUS CHART NAMESPACE
data8-jupyterhub 11 Thu Mar 8 10:10:59 2018 DEPLOYED jupyterhub-v0.7-e6b48f6 kube-public
如果更改了config.yaml文件可以使用下面命令滚动升级。
helm upgrade data8-jupyterhub ./jupyterhub --version=v0.7-e6b48f6 -f config.yaml
如果要删除这次的部署,使用下面的命令。
helm del --purge data8-jupyterhub
最后一步就是打开浏览器,输入的域名就是在jupyterhub-ingress-ui.yaml中的host的值,没有外部DNS的话,就在自己机器添加hosts文件,然后访问。